Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- HashTable
- 재귀
- Medium
- leetcode
- matrix
- 중간
- 미디움
- tree
- sorting
- math
- dfs
- 쉬움
- Depth-first Search
- recursive
- two pointers
- backtracking
- 리트코드
- easy
- hash table
- string
- 문자열
- binary search
- linked list
- binary tree
- Python
- list
- DP
- Binary
- 이진트리
- Array
Archives
- Today
- Total
부부의 코딩 성장 일기
LeetCode 257(Binary Tree Paths, Python) 본문
1. 문제 링크
LeetCode - The World's Leading Online Programming Learning Platform
Level up your coding skills and quickly land a job. This is the best place to expand your knowledge and get prepared for your next interview.
leetcode.com
2. 문제 설명
- binary tree의 root가 주어졌을 때, root부터 leaf까지 가는 모든 paths를 list에 append하여 반환
- 여기서 leaf란 children이 없는 node를 뜻함
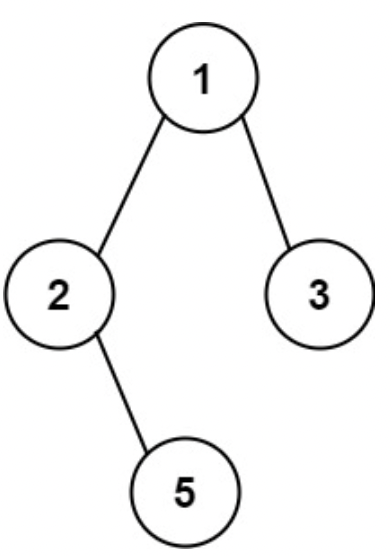
- 예시1) 트리가 아래와 같다면, path는 1->2->5, 1->3이 존재하며, 이에 ["1->2->5", "1->3"]을 반환
- 예시2) root = [1]이라면 그 자체가 node이면서 leaf이므로, ["1"] 반환
3. 처음 풀이
- backtrack을 사용해서
- output = [] 라는 빈 list에 path가 완성될 때마다, 해당 path를 append하는 구조로 코드를 작성했다.
- 만약 root가 None이면 그냥 그대로 return하고,
- root는 None이 아닌데, root.right와 root.left가 None이라면,
- root.val을 path에 append하고, 이건 leaf 까지 도달한 것이므로, output.append(path.copy())를 하였고,
- 그 외의 경우에 대해서는,
- 우선 root.val을 append하고,
- root.left에 대해 backtrack 한 뒤 path를 다시 pop
- root.right에 대해 backtrack 한 뒤 path를 다시 pop 하는 것으로 작성하였다.
- 그러면 모든 경우에 대해 output 리스트에 path가 쌓이게 된다.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def binaryTreePaths(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[str]:
output = []
def backtrack(root,path):
if root is None:
return
if root.right is None and root.left is None:
path.append(str(root.val))
output.append(path.copy())
return
path.append(str(root.val))
if root.left:
backtrack(root.left, path)
path.pop()
if root.right:
backtrack(root.right, path)
path.pop()
backtrack(root,[])
answer = []
for i in output:
answer.append("->".join(i))
return answer
4. 다른 풀이
- 아래처럼 새로운 함수를 binaryTreePaths에 만들지 않고,
- self.binaryTreePaths(root.left) + self.binaryTreePaths(root.right)를 for문을 돌리면서 최종 path를 업데이트 하여 반환하는 코드도 있었다.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def binaryTreePaths(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[str]:
# If the root is None, return an empty list
if not root:
return []
# If the node is a leaf, return the value of the node as the path
if not root.left and not root.right:
return [str(root.val)]
# Get all paths from the left and right subtrees
paths = []
for path in self.binaryTreePaths(root.left) + self.binaryTreePaths(root.right):
# For each path, prepend the current node's value
paths.append(str(root.val) + '->' + path)
return paths'Algorithm > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LeetCode 258(Add Digits, Python) (0) | 2024.02.20 |
|---|---|
| LeetCode 98(Validate Binary Search Tree, Python) (0) | 2024.02.19 |
| LeetCode 97(Interleaving String, Python) (0) | 2024.02.17 |
| LeetCode 242(Valid Anagram, Python) (0) | 2024.02.16 |
| LeetCode 234(Palindrome Linked List, Python) (0) | 2024.02.15 |
