Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- string
- dfs
- two pointers
- binary search
- HashTable
- 쉬움
- 문자열
- backtracking
- list
- 중간
- tree
- Binary
- Array
- 리트코드
- leetcode
- 재귀
- DP
- 이진트리
- Medium
- Python
- sorting
- Depth-first Search
- matrix
- 미디움
- recursive
- math
- linked list
- easy
- binary tree
- hash table
Archives
- Today
- Total
부부의 코딩 성장 일기
LeetCode 63(Unique Paths II, Python) 본문
1. 문제 링크
Unique Paths II - LeetCode
Can you solve this real interview question? Unique Paths II - You are given an m x n integer array grid. There is a robot initially located at the top-left corner (i.e., grid[0][0]). The robot tries to move to the bottom-right corner (i.e., grid[m - 1][n -
leetcode.com
2. 문제 설명
- mxn 정수 array인 grid가 주어져있고, robot이 초기에 좌측 상단에 위치해 있다.
- 로봇이 우측 하단으로 이동하려 하며, 오른쪽 혹은 아래로만 이동할 수 있다.
- 이 때 장애물은 1, 이동가능 공간은 0으로 marked 되어있고, 로봇은 장애물을 포함한 경로로 이동할 수 없다.
- 이 때, 가능한 unique path의 수를 반환해라.
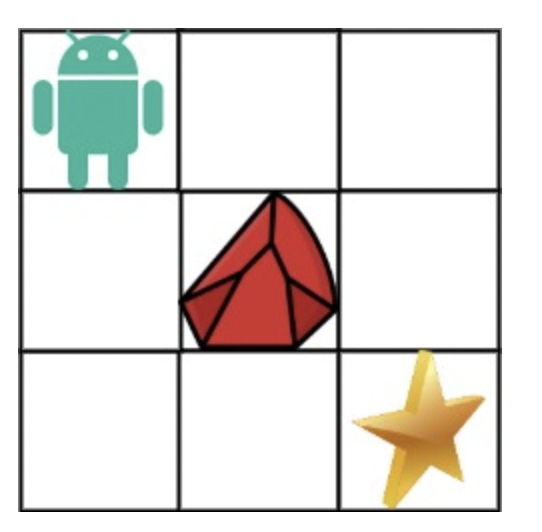
- 예시1) 로봇은 장애물을 피해서 별까지 이동해야 할 때,
- 가능한 경로는, 오른쪽→오른쪽→아래→아래 로 이동하거나
- 아래→아래→오른쪽→오른쪽 으로 이동하는 방법 뿐으로 결과적으로 2를 반환한다.
3. 처음 풀이
- 학창시절 배웠던, 최단 경로 path개수 구하기에서, 장애물이 있는 버전이다.
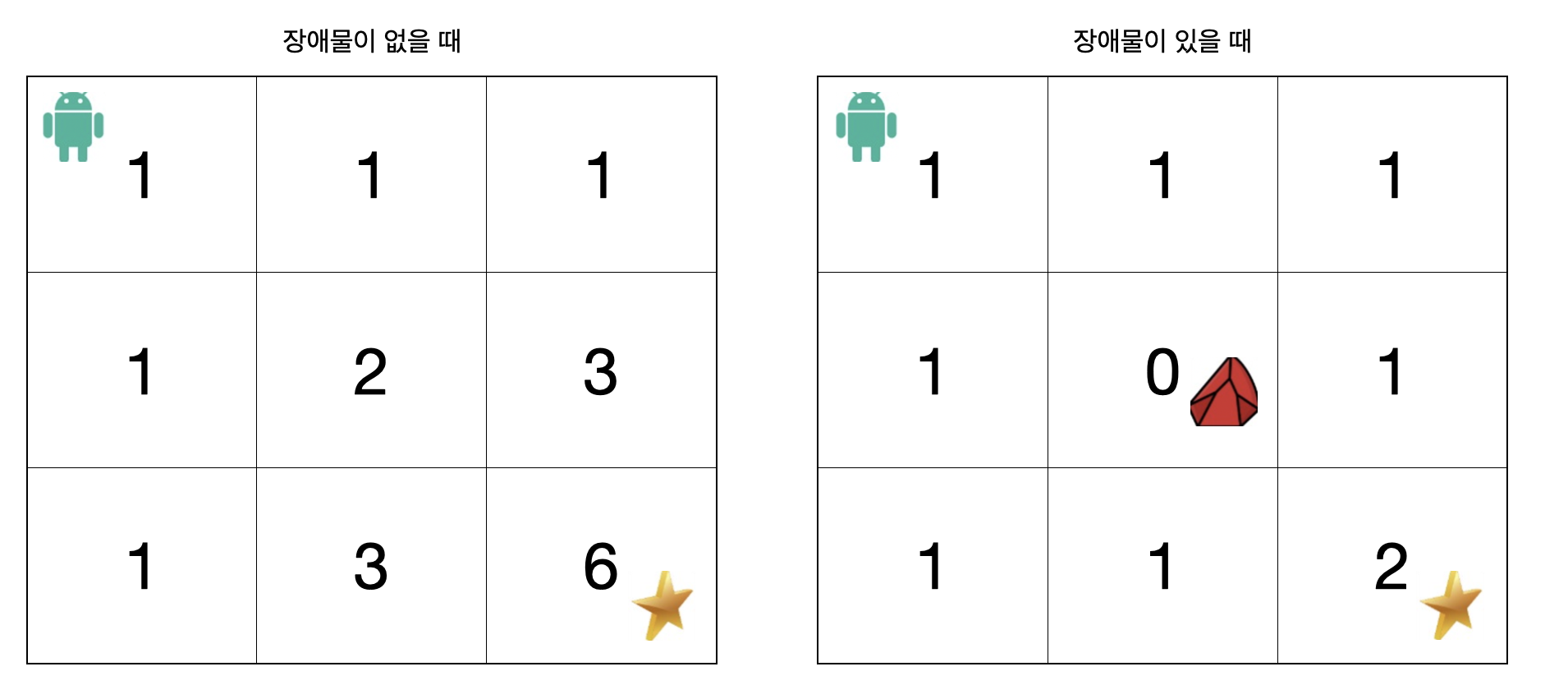
- combination을 통해 계산할 수도 있지만, 아래처럼 각 위치 까지 갈 수 있는 경우의 수를 계산한 후,
- 인접한 두 면의 경우의수를 합하면서 표를 채워나가면,
- 아래 케이스에서는 장애물이 없을 때 6가지의 경로가 존재하고, 장애물이 있을 때 2가지의 경로가 존재한다.
- 결국 각 위치까지의 경로의 경우의 수를 파악하고, (부분의 합), 전체 경우의 수를 판단하는 Dynamic Programming 문제이다.
- obstacleGrid에 위의 값을 채워나가는 방식으로 코드를 작성하였다.
- 장애물을 만나면 값을 0으로 셋팅
- 1행 1열은 (장애물이 아니면) 1로 셋팅
- 첫 번째 가로줄 채우기
- 직전이 0이면 현재도 0으로, 아니면 1로 채우기
- 첫 번째 세로줄 채우기
- 직전이 0이면 현재도 0으로, 아니면 1로 채우기
- 마지막으로는, 인접한 두 면의 합산 값을 채우기
- obstacleGrid[c-1][r] + obstacleGrid[c][r-1]
- 가장 마지막 value 반환 (obstacleGrid[-1][-1])
- runtime 90% 정도로 나쁘지 않았음.
class Solution:
def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
for c, col in enumerate(obstacleGrid):
for r, row in enumerate(col):
if row == 1:
obstacleGrid[c][r] = 0
elif c == 0 and r == 0:
obstacleGrid[c][r] = 1
elif c == 0:
obstacleGrid[c][r] = 0 if obstacleGrid[c][r - 1] == 0 else 1
elif r == 0:
obstacleGrid[c][r] = 0 if obstacleGrid[c - 1][r] == 0 else 1
else:
obstacleGrid[c][r] = obstacleGrid[c - 1][r] + obstacleGrid[c][r - 1]
return obstacleGrid[-1][-1]4. 다른 풀이
- backtracking으로 해결한 풀이도 있었음
class Solution:
def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def backtracking(i,j):
if i == gr - 1 and j == gc - 1:
return 1 if obstacleGrid[i][j] != 1 else 0
if i == gr or j == gc or obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1: return 0
if (i,j) in memo: return memo[(i,j)]
memo[(i,j)] = backtracking(i+1,j) + backtracking(i,j+1)
return memo[(i,j)]
gr = len(obstacleGrid)
gc = len(obstacleGrid[0])
memo = {}
return backtracking(0,0)
5. 배운 점
- 어떤 알고리즘을 사용하면 좀 더 효율적으로 풀 수 있을지 고민하기.
'Algorithm > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LeetCode 71(Simplify Path, Python) (0) | 2024.01.18 |
|---|---|
| LeetCode 64(Minimum Path Sum, Python) (0) | 2024.01.17 |
| LeetCode 62(Unique Paths, Python) (0) | 2024.01.15 |
| LeetCode 61(Rotate List, Python) (1) | 2024.01.14 |
| LeetCode 59(Spiral Matrix II, Python) (1) | 2024.01.13 |



